Scoliosis - Treatments, Causes, Symptoms, Home Remedies & More
Written By: Dr. Thaer Darwish
Updated On:December 22, 2023
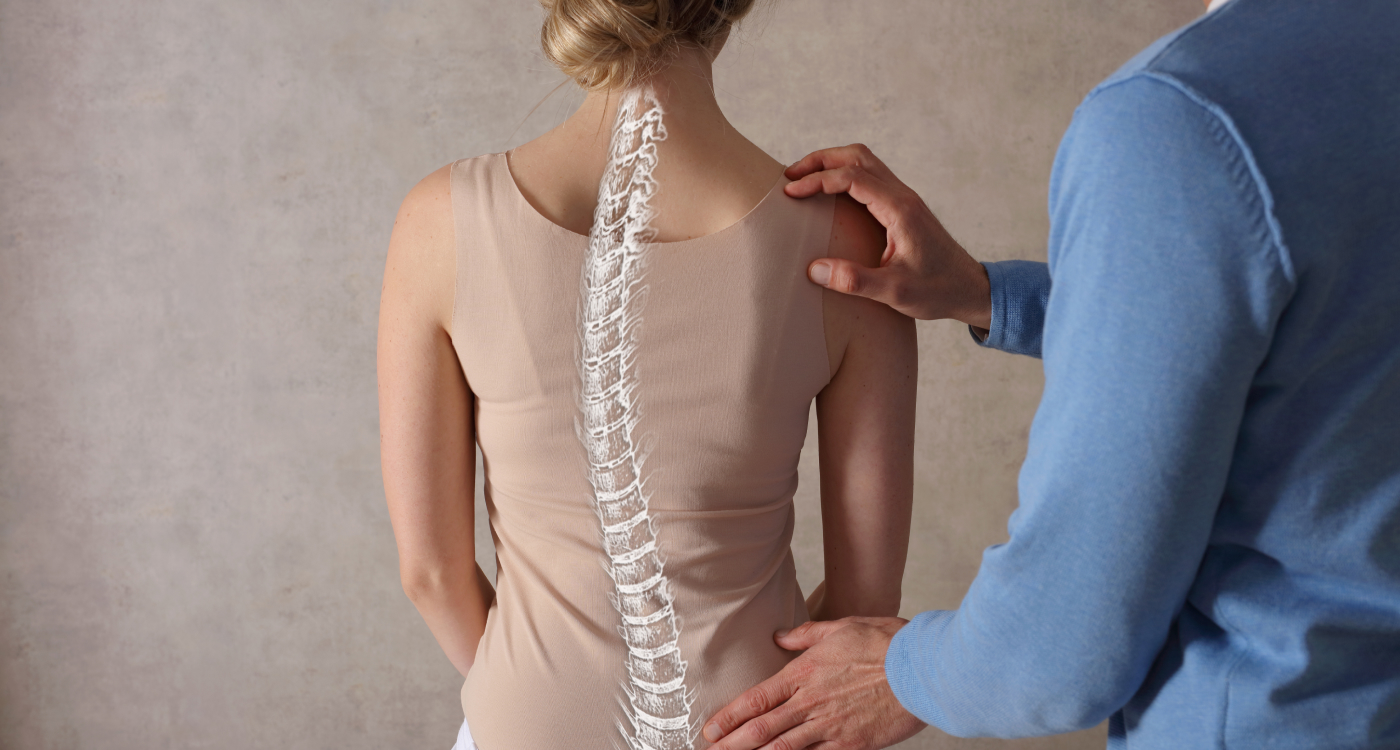
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis refers to the sideways curvature of the spine. It usually occurs during childhood or adolescence and more specifically as one approaches puberty.
Types of Scoliosis
There are various different types of scoliosis, such as:
- Congenital Scoliosis: This is a type of scoliosis that a person is born with. It is caused when the spine does not develop properly in the womb.
- Early onset scoliosis: A curve in the spine appears between age 10 and puberty.
- Adult degenerative scoliosis: This type of scoliosis is divided into two categories:
- De novo scoliosis: Caused by wear and tear and first appears during adulthood.
- Degenerative scoliosis: This type of scoliosis affects adults with a history of scoliosis. It can cause the spine to collapse due to repetitive wear and tear with age.
- Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Commonly occurs in individuals between the ages of 10 and 18.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: This type of scoliosis is caused by neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy.
- Syndromic scoliosis: This is when a curvature of the spine appears as part of a syndrome.
Scoliosis in Men and Women
It has been reported that idiopathic scoliosis occurs ten times more often in girls than it does in boys over the age of ten. Girls are also more likely to develop worse curves from the condition than boys. Upon diagnosis, the chances of a girl’s scoliosis worsening is up to eight times more likely than boys.
Scoliosis Causes
Although the cause for common or idiopathic scoliosis is not clear, most doctors believe that hereditary factors play a key role. Other forms of scoliosis can be caused by birth defects, neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy, infection, tumors and muscular dystrophy. Scoliosis can also be caused by a spinal injury.
Scoliosis Risk factors
Factors that affect an individual’s chances of developing the most common type of scoliosis are:
- Age: Idiopathic scoliosis is most likely to appear during the growth spurt just before puberty.
- Gender: Boys and girls tend to develop moderate scoliosis at the same pace, but the curve is more likely to worsen in girls, requiring more extensive scoliosis treatment.
- Family history: Scoliosis can affect individuals with a family history of the condition.
Symptoms of Scoliosis
Signs and symptoms of scoliosis in children:
- Uneven hips, like one being higher than the other
- Their ribs may protrude outwards
- Their shoulders may be at two different heights
- The distance between their arms and legs when standing upright may be unequal
- Muscles in their lower back may be more noticeable, causing a bump to appear
- Irregular skin folds at their waist
Signs and symptoms of scoliosis in adults:
- Back pain
- Uneven shoulders
- Uneven hips
- Protrusion or bump in the lower back
- Difficulty in standing upright
- Feeling tired
- Numbness and weakness in the legs
When to see a doctor for Scoliosis
If you are experiencing back pain or have asymmetrical hips, you should get yourself checked for scoliosis. Mild curves in the spine can go unnoticed until the condition has progressed significantly.
Complications of Scoliosis
Complications of scoliosis can include:
- Back pain: Adults with scoliosis are very likely to experience chronic back pain.
- Damage to thoracic organs: Scoliosis can often cause the rib cage to press against the heart and lungs, leading to damage of these organs.
- Breathing problems: If scoliosis is left untreated, the progressing curvature of the spine can limit lung capacity, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Leg pain: In advanced cases, hips can become misaligned causing one leg to appear shorter than the other. The misalignment causes certain muscles to overcompensate for balance, hence causing them to tire sooner.
- Lumbar stenosis: This condition is the constriction of the spinal canal, which causes nerve complications, weakness, and pain in the lower limbs.
- Change in physical appearance: As scoliosis deteriorates, it causes noticeable changes in an individual’s physical appearance such as uneven hip, shoulders, etc.
Scoliosis Treatment
Whilst mild scoliosis may not require medical intervention, moderate to severe cases will most likely need surgery. Depending on the type of scoliosis a patient has, a variety of scoliosis treatments are available, including:
- Painkillers: These can help relieve the back and leg pain caused by scoliosis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) are the most commonly recommended scoliosis treatment.
- Exercise: This involves stretching and movement of the back to help relieve symptoms associated with scoliosis and improve spinal flexibility.
- Spinal injections: Scoliosis can lead to pain or numbness caused by the application of pressure on nerves around your spine. Injections of steroids or local anesthetic into the back can help relieve these symptoms.
- Back braces: Supportive devices such as back braces can help relieve stress and pressure on the spine in adults with scoliosis. This is the preferred scoliosis treatment option for children with scoliosis as it prevents the curve from worsening and improves deformity.
- Surgery: Surgical procedures for treatment of scoliosis and associated symptoms include:
- Laminectomy: This procedure involves the removal of a section of a vertebra to alleviate pressure on a certain nerve.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves the removal of a section of an intervertebral disc to alleviate pressure on a certain nerve.
- Spinal fusion: This procedure involves the amalgamation of two or more vertebrae to straighten the spine.
Scoliosis Prevention
Degenerative scoliosis, which is caused by poor posture or trauma, can be prevented. While trauma itself is difficult to prevent, poor posture can easily be corrected over time, by:
- Reducing the asymmetric stress caused by activities such as carrying a heavy backpack on one shoulder.
- Practicing good posture by keeping your head squared with your shoulders.
- Using an ergonomic chair at work to adapt your seating position to your unique needs.
- Avoiding a sedentary lifestyle.
- Strengthening muscles that will support good posture by exercising regularly.
- Taking good care of bone health with a nutritious diet as well as regular exercise, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
What is Kyphosis?
Kyphosis, commonly known as ‘hunchback’, is a spinal disorder which causes abnormal rounding of the upper back. Typically, it is more common in women and can occur at any age. Age-related kyphosis occurs due to gradual weakening of the vertebrae that can cause them to compress or crack over time. Moderate kyphosis does not cause many issues but severe kyphosis can lead to pain and deformity.
Complications of Kyphosis
Age-related kyphosis is associated with weakening of back muscles leading to difficulty in movements such as walking, standing upright, etc. The spinal curvature caused by this condition can also lead to pain when lying down. Severe kyphosis can cause damage to the lungs and digestive tract by applying excessive pressure on them. This can lead to breathing and digestive problems.
How are Kyphosis and Scoliosis Different?
While both terms describe the occurrence of an abnormal curvature in the spine, it is important to note that the direction of this curvature differs in both conditions. Kyphosis refers to the forward bending or curvature of the upper spine while scoliosis refers to the sideways curvature of the spine. Kyphosis, therefore leads to a hunchback or slouching posture while scoliosis leads to a ‘c-shaped’ or ‘s-shaped’ curve of the back.
For more information on the causes, diagnosis and treatment of scoliosis, get in touch with us.
Meet our doctors from the Neurology department