Appendicitis
Written By: Dr. Szabolcs Papp
Updated On:December 26, 2023

The appendix is a vestigial organ and it is not really understood what it does in the body. The finger-like organ at the beginning of the colon does not play any active role in the maintenance of homeostasis in the body. Due to this, removing it does not make a difference in the health and quality of life of the person.
However, not everyone gets their appendix removed, the procedure is dedicated to those who suffer from appendicitis.
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is a painful inflammation of the appendix. This inflammation can cause debilitating symptoms that often require urgent medical intervention.
Most people only undergo the removal of the appendix due to appendicitis that has already worsened and is at risk for complications.
What are the Symptoms of Appendicitis?
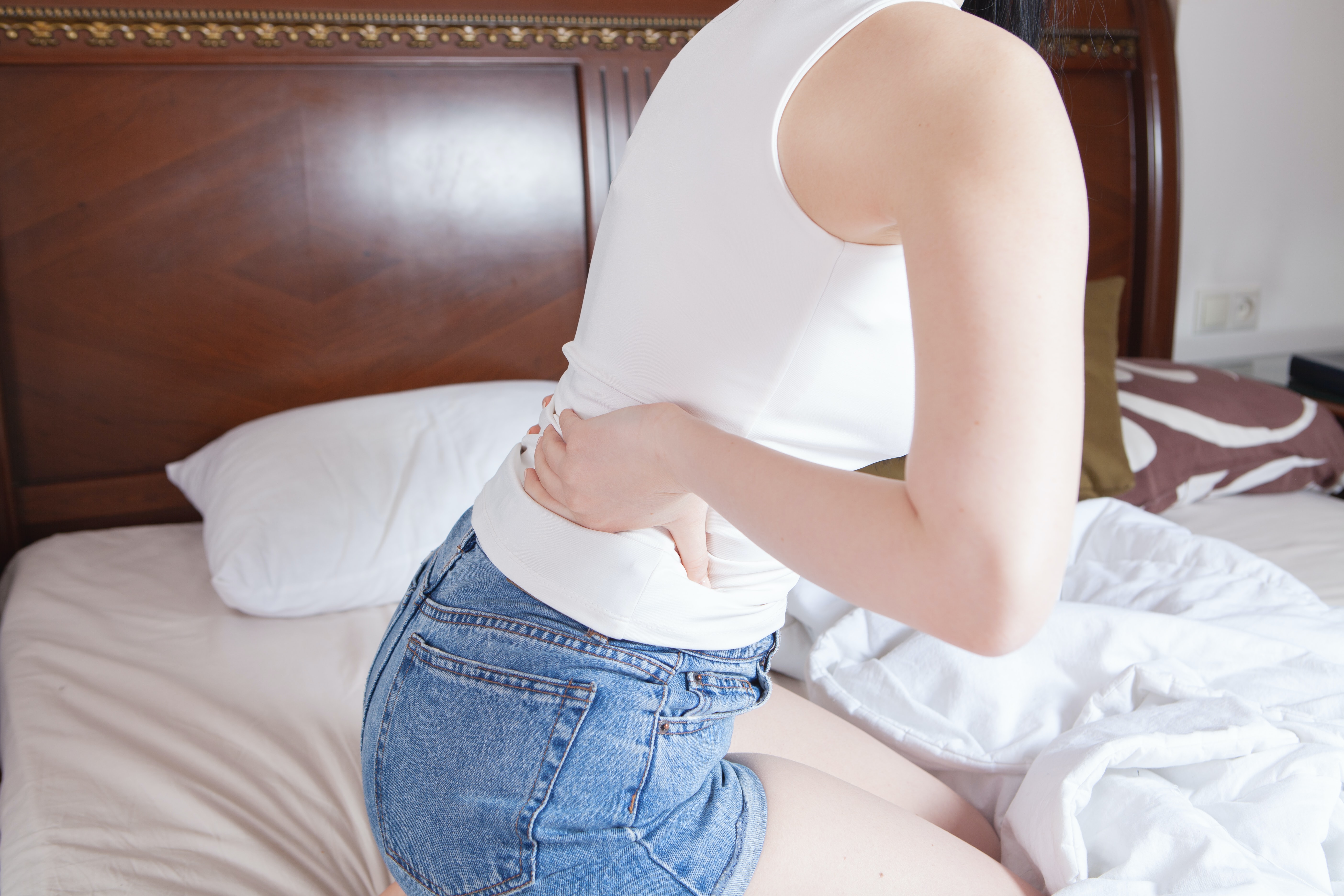
Typically, the main symptom of appendicitis is abdominal pain that starts around the belly button. This pain gradually moves from the centre of the abdomen to the right lower corner of the abdomen. In fact, the presence of pain in this area, during the physical examination done by the physician, is diagnostic for appendicitis. However, the exact site of pain is subject to change based on the age and gender of the patient.
Other appendicitis symptoms include:
- Sudden onset of abdominal pain
- High fever that started as a low-grade fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Bloating and flatulence
Causes of Appendicitis
The leading cause of appendicitis is the blockage of the appendix. However, the mechanism is not fully understood. Sometimes, appendicitis is caused by obstruction of the appendix by faecal matter from the colon. In such cases, it is referred to as fecalith appendicitis. Sometimes, an infection in the body such as an upper respiratory infection can cause the lymph nodes in the body to swell. When lymph nodes in the appendix are swollen, they can obstruct the appendix, resulting in appendicitis. Most of the time, the obstruction and inflammation of the appendix are believed to be idiopathic, meaning their cause is not understood or known.
When to Visit a Doctor for Appendicitis?
The appendix is not an essential organ in the body, but appendicitis and its complications can be severe on the body and have a significantly negative impact on overall health. It is essential to seek medical help if you are experiencing sudden abdominal pain or abdominal pain that worsened drastically in a short period of time. If you were experiencing abdomen pain that resolved spontaneously and got worse again, then you should seek immediate medical help as there is a possibility that the appendix had burst.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
The diagnosis of the condition requires a visit to the doctor, who might order a few tests to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Physical Test.
- It will assess your pain. Your doctor will put gentle pressure on the affected area and when the pressure is released, you will feel significantly worsened pain. This worsening pain is a sign of appendicitis.
Digital Rectal and pelvic exam.
- The doctor will make sure that prostate and other rectal issues are not the cause of the abdominal pain. Women will need to undergo a pelvic test to rule out a gynaecological disorder as the cause of pain.
Blood test.
- This is done to check for elevated white blood cells which are indicative of an infection.
Urinalysis.
- To check for UTI or a kidney stone as they may present with similar symptoms to appendicitis.
Imaging test.
- Your doctor will recommend an abdominal ultrasound and CT to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis, especially if the tests and symptoms produce non-conclusive results.
Treatment of Appendicitis
Appendicitis treatment involves the removal of the inflamed appendix. Surgical excision of the appendix is known as an appendectomy. Surgery is the ultimate appendicitis treatment and can be performed either laparoscopically or using open surgical techniques. The decision between the two different types of surgery will be made by the surgeon.
Laparoscopic surgery allows quick recovery and has minimal scarring, compared to open appendectomy (appendix surgery) . Before the surgery, however, patients may have to undergo an antibiotic regime to treat the underlying infection. In some cases, antibiotic therapy is sufficient to produce results and treat appendicitis.
Severe cases of appendicitis that are at risk of bursting require urgent surgery. In case the appendix has already burst, an open appendectomy procedure will need to be performed. This is because the contents of the appendix can burst into the entire abdomen, and a laparoscopic surgery would not be able to appropriately remove the contents.
In cases where an appendix has burst before medical intervention was sought, there is a risk of abscess formation. If an abscess forms, then a draining tube will be placed through the skin to clear out the abscess. The burst appendix and its content can be removed surgically after the abscess has been treated completely.
This revision incorporates the keyword "appendicitis treatment" in a natural and relevant manner, enhancing the paragraph's SEO effectiveness while maintaining clarity and readability.
Meet our doctors from the Gastroenterology department